Chinese doctors have transplanted a pig’s kidney with multiple gene edits into a brain-dead human recipient, just weeks after the same team performed the world’s first pig liver transplant on a human.
The latest operation was the first of its kind in China and follows previous transplants in the United States.
“As of April 7, the transplanted kidney has been working continuously for 13 days,” Qin Weijun, director of the Air Force Medical University Xijing Hospital, told Science and Technology Daily on Monday.
Do you have questions about the biggest topics and trends from around the world? Get the answers with SCMP Knowledge, our new platform of curated content with explainers, FAQs, analyses and infographics brought to you by our award-winning team.
“It is functioning well in the recipient’s body and producing urine normally.”
The transplant was conducted on March 25, only a couple of weeks after the team performed the pig liver transplant. In both cases the patients’ families agreed to the procedure to help advance medical science, the university said.
Kidney transplants are the only cure for end-stage kidney disease. Although over a million patients in China suffer from the condition, only 10,000 transplants are performed every year, the Air Force Medical University’s department of urology said in a WeChat post last week.
However, xenogenic transplants – the transplant of an organ or tissues from one species into another – could offer a solution.
Pig organ transplants in China and the US open an ethical can of worms
Pigs are used for these operations because they have similar metabolisms and organ size to humans. While monkeys are the most similar species to humans, the US Food and Drug Administration has banned the use of their organs because of the higher risk of disease spreading.
Medical teams in both China and the US have tested pig organ transplants on brain-dead patients who need a ventilator to survive, with the consent of their families, before trying the technology on other patients.
“Research on xenogenic organ transplantation has entered an accelerated period,” said Dou Kefeng, one of the transplant team leads, according to the post.
Such transplants can provide “a highly imaginative solution” to transplant organ shortages, even just by buying time for patients waiting for human organs, Dou said.
During the transplant, the renal artery of the pig’s kidney was connected to the patient’s external iliac artery, which provides blood supply to the legs.
Once the blood flow resumed and the kidney began producing urine, the patient’s own kidneys were removed, the university said.
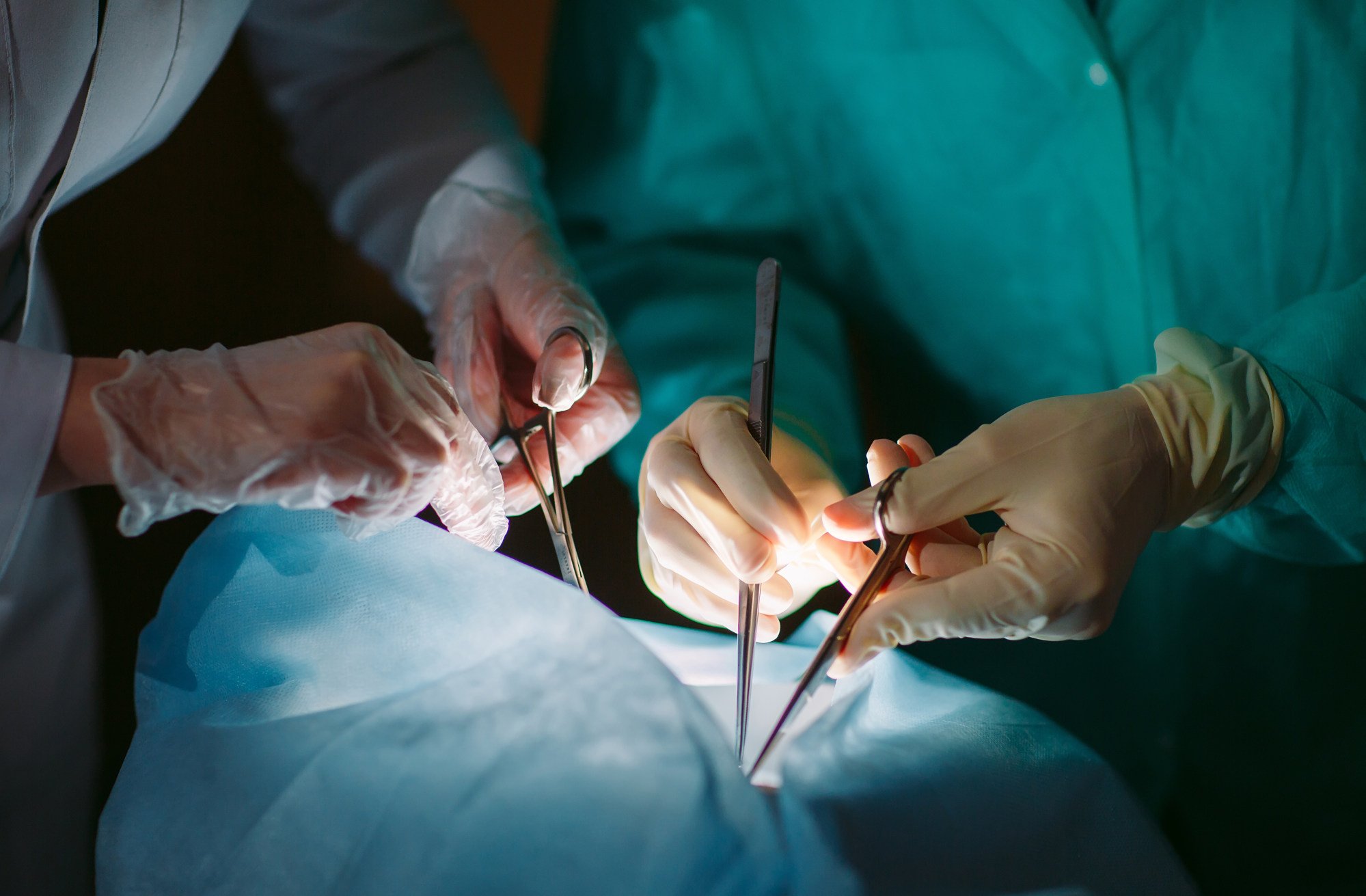
One of the major ethical concerns with xenotransplantation is the risk of acute rejection as well as the transfer of infectious diseases between the donor animal and humans.
To reduce that risk, the scientists used CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing technology to add two human genes to the pig used in the transplant and remove three pig genes that can cause hyperacute rejection, the university said.
Last month, a team from the Massachusetts General Hospital in the United States made history with the first transplant of a gene-edited pig kidney into a non-brain-dead patient with end-stage kidney disease.
The 62-year-old recipient suffered an episode of acute rejection eight days after the transplant when white blood cells infiltrated the organ, according to US medical site STAT news.
However, this type of rejection is common in human kidney transplants and the report said the patient was successfully treated with steroids and a drug to deplete the white blood cells.
The doctors in China had been monitoring their kidney recipient for signs of rejection or infection, the university said.
The team’s feat with a pig liver last month, which also functioned normally for 10 days until it was removed, posed a bigger challenge than their recent success, because human livers are more complex than kidneys in both function and structure which means they cannot be completely replaced by a pig’s organ.
The Chinese team chose to keep the recipient’s own liver alongside the transplant to address this issue.
Chinese team grows humanised kidneys in pigs, raising hopes and ethical concerns
Before their attempts with humans, the transplant team also transplanted pig organs into monkeys in 2020, the university said.
Qin said that the transplant team’s work could pave the way for future transplants that could help the millions waiting for life-saving operations.
More from South China Morning Post:
- Chinese patient receives world’s first gene-edited pig liver transplant
- Patients in China and the US have received pig organ transplants, opening an ethical can of worms
- ‘New way of thinking’: Chinese researchers unveil unique strategy for tissue regeneration, function
For the latest news from the South China Morning Post download our mobile app. Copyright 2024.





