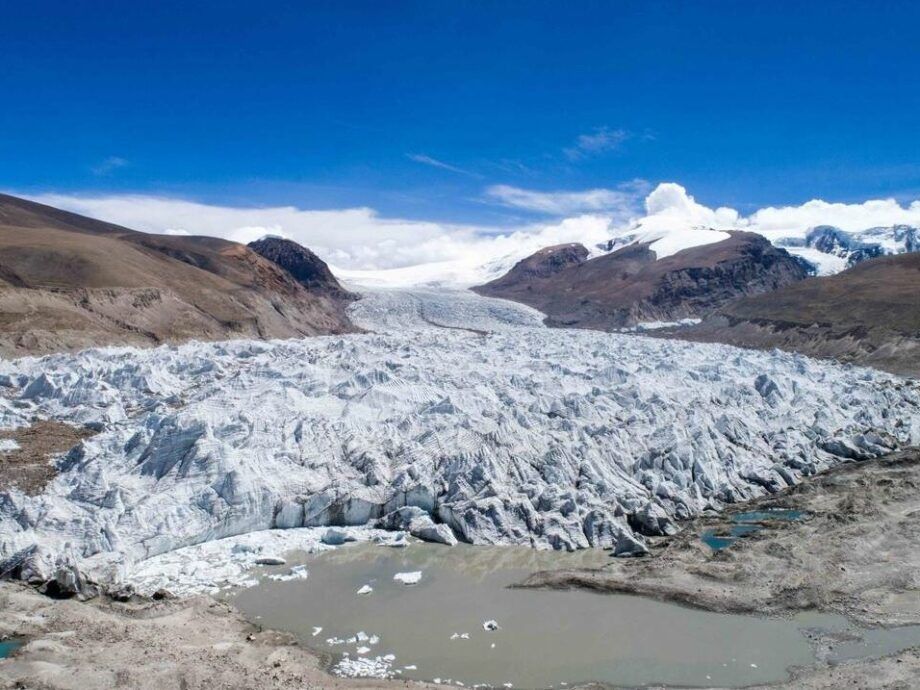
Tons of trash and several bodies remain on the icy slopes of the world's highest mountain. - AP
KATHMANDU: The highest camp on the world’s tallest mountain is littered with garbage that is going to take years to clean up, according to a Sherpa who led a team that worked to clear trash and dig up dead bodies frozen for years near Mount Everest’s peak.
The Nepal government-funded team of soldiers and Sherpas removed 11 tonnes of garbage, four dead bodies and a skeleton from Everest during this year's climbing season.
Ang Babu Sherpa, who led the team, said there could be as much as 40-50 tonnes of garbage still at South Col, the last camp before climbers make their attempt on the summit.
"The garbage left there was mostly old tents, some food packaging and gas cartridges, oxygen bottles, tent packs, and ropes used for climbing and tying up tents,” he said, adding that the garbage is in layers and frozen at the 8,000m altitude where the South Col camp is located.
Since the peak was first conquered in 1953, thousands of climbers have scaled it and many have left behind more than just their footprints.
In recent years, a government requirement that climbers bring back their garbage or lose their deposits, along with increased awareness among climbers about the environment, have significantly reduced the amount of garbage left behind. However, that was not the case in earlier decades.
"Most of the garbage is from older expeditions,” Ang Babu said.
The Sherpas on the team collected garbage and bodies from the higher-alttitude areas, while the soldiers worked at lower levels and the base camp area for weeks during the popular spring climbing season, when weather conditions are more favorable.
Ang Babu said the weather was a big challenge for their work in the South Col area, where oxygen levels are about one-third the normal amount, winds can quickly turn to blizzard conditions and temperatures plunge.
"We had to wait for good weather when the sun would melt the ice cover. But waiting a long time in that altitude and conditions is just not possible,” he said. "It's difficult to stay for long with the oxygen level very low.”
Digging out the garbage is also a big task, since it is frozen inside ice and breaking the blocks is not easy.
It took two days to dig out one body near the South Col which was frozen in a standing position deep in the ice, he said. Part way through, the team had to retreat to lower camps because of the deteriorating weather, and then resume after it improved.
Another body was much higher up at 8,400m and it took 18 hours to drag it to Camp 2, where a helicopter picked it up.
The bodies were flown to Tribhuvan University Teaching Hospital in Kathmandu for identification.
Of the 11 tonnes of garbage removed, three tonnes of recovered waste were taken to villages near Everest's base and the remaining eight were carried by porters and yaks and then taken by trucks to Kathmandu. There it was sorted for recycling at a facility operated by Agni Ventures, an agency that manages recyclable waste.
"The oldest waste we received was from 1957, and that was rechargeable batteries for torch lights,” said Sushil Khadga of the agency.
Why do climbers leave garbage behind?
"At that high altitude, life is very difficult and oxygen is very low. So climbers and their helpers are more focused on saving themselves," Khadga said. - AP