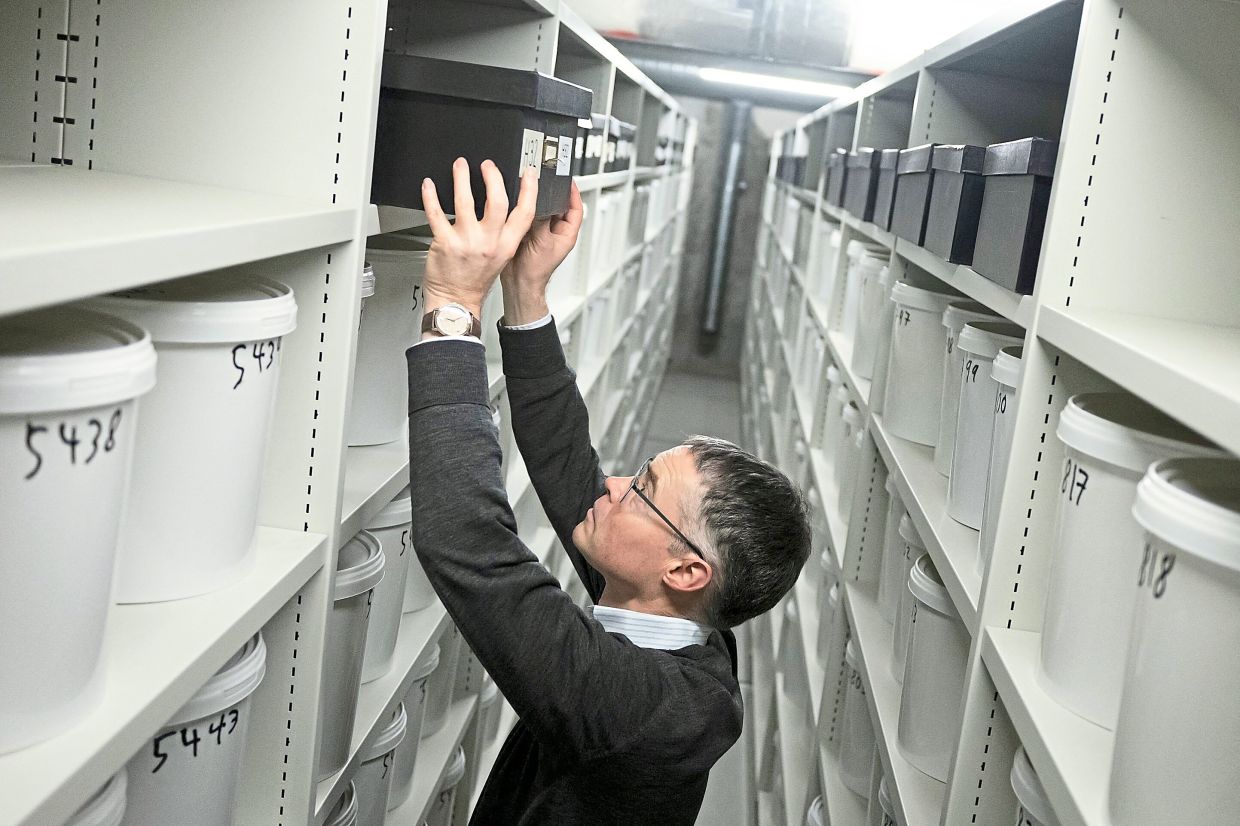
Dr Wirenfeldt Nielsen reaches for a box amidst the world's largest collection of preserved brains from deceased mental health patients in the basement of the University of Southern Denmark. — AFP
Countless shelves line the walls of a basement at the University of Southern Denmark, holding what is thought to be the world's largest collection of brains.
There are 9,479 of the organs, all removed from the corpses of mental health patients over the course of four decades until the 1980s.
Save 30% for ads-free and full access now!