A sweeping series of plantation closures in Hawaii allowed highly flammable non-native grasses to spread on idled lands, providing the fuel for huge blazes. — ©2023 The New York Times Company
WHEN Hawaii’s last sugar cane plantation shut down in Maui in 2016, it marked the end of an era when sugar reigned supreme in the archipelago’s economy. But the last harvest at the 14,500ha plantation underscored another pivotal shift: the relentless spread of extremely flammable, non-native grasses on idle lands where cash crops once flourished.
Varieties such as guinea grass, molasses grass and buffel grass — which originated in Africa and were introduced to Hawaii as livestock forage — now occupy nearly a quarter of Hawaii’s landmass. Fast growing when it rains and drought resistant when lands are parched, such grasses are fueling wildfires across Hawaii, including the recent deadly blaze in Maui.
Get 30% off with our ads free Premium Plan!
A fiery hell
A helicopter drops water on hot spots in a wildfire that burned several homes in Kula, Hawaii, on Aug 10. — Photos: ©2023 The New York Times Company
A helicopter drops water on hot spots in a wildfire that burned several homes in Kula, Hawaii, Aug. 10, 2023. (Max Whittaker/The New York Times)
Firefighters spray water on a hot spot caused by wildfires in Lahaina.
Firefighters spray water on a hot spot caused by wildfires in Lahaina, Hawaii, Aug. 10, 2023. (Philip Cheung/The New York Times)
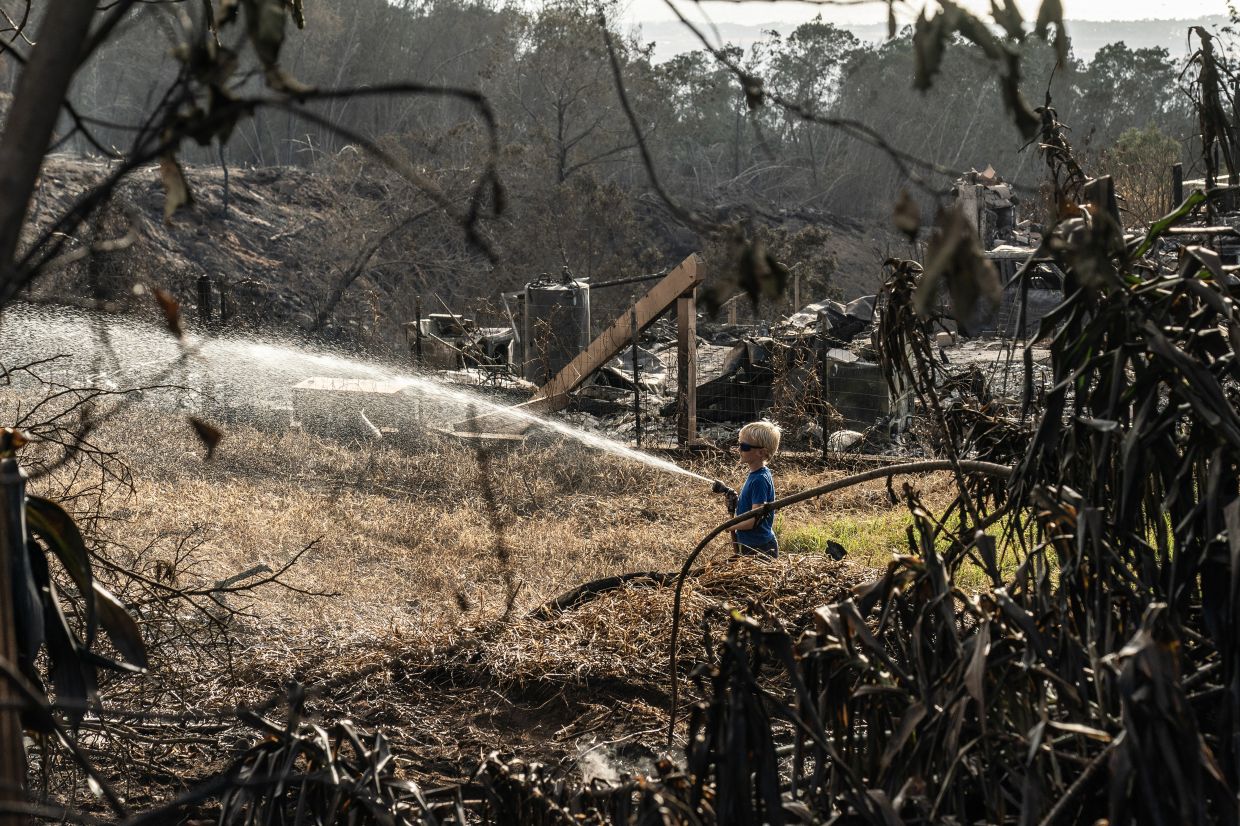
Misha Fehlmann spraying water to put out hot spots in Kula.
Misha Fehlmann sprays water to put out hot spots in Kula, Hawaii, Aug. 12, 2023. (Go Nakamura/The New York Times)
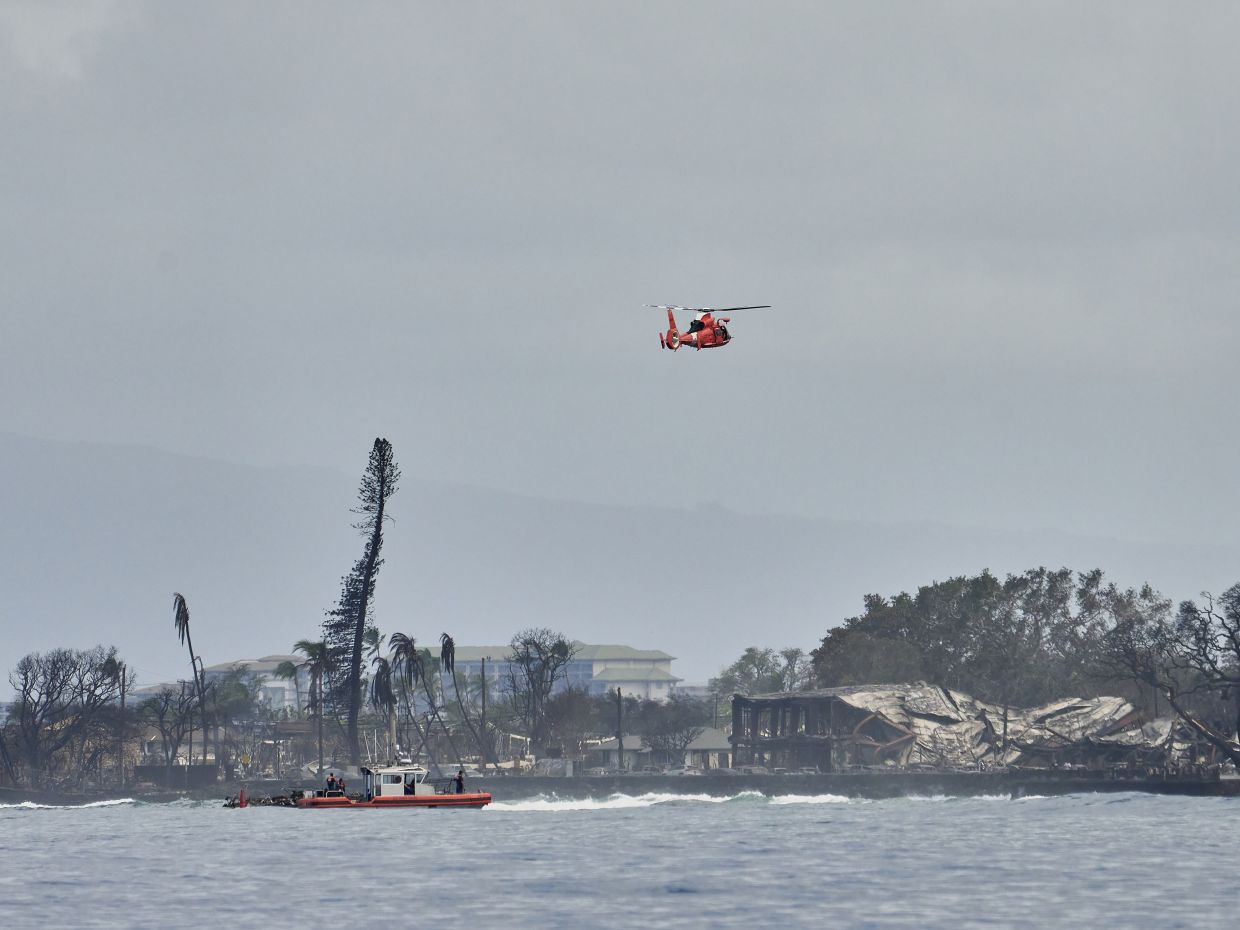
A coastguard helicopter and boat pass over damage caused by wildfires in Lahaina.
A coastguard helicopter and boat pass over damage caused by wildfires in Lahaina, Maui, Hawaii, Aug. 10, 2023. (Philip Cheung/The New York Times)
The town of Lahaina, Hawaii, after the wildfire.
The town of Lahaina, Hawaii, after the wildfire, on Aug. 11, 2023. (Max Whittaker/The New York Times)
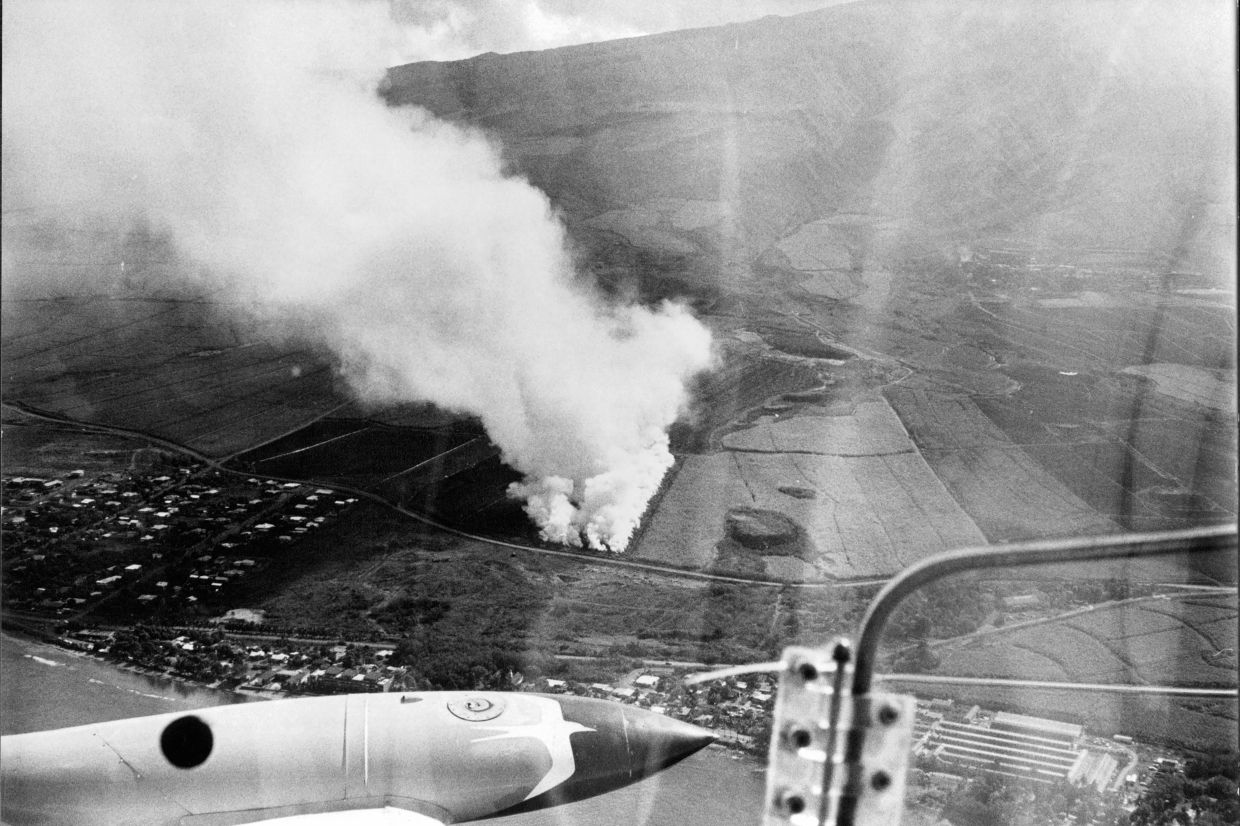
A plume of smoke rising from burning sugar cane fields before harvest in Maui, Hawaii, March 3, 1970. — Filepic/©2023 The New York Times Company
A plume of smoke rising from burning sugar cane fields before harvest in Maui, Hawaii, March 3, 1970. (Wallace Turner/The New York Times)











